Understanding LED Drivers: Essential Components for LED Lighting Systems
In recent years, LED technology has revolutionized the lighting industry. With its energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and superior performance, LED lighting has become the go-to solution for residential, commercial, and industrial lighting applications. However, despite its many advantages, LED lighting systems require specific components to function correctly, and one such critical component is the LED driver. Understanding the role and functionality of LED drivers is essential for both consumers and professionals who are looking to get the most out of their LED lighting systems.
What Is an LED Driver?
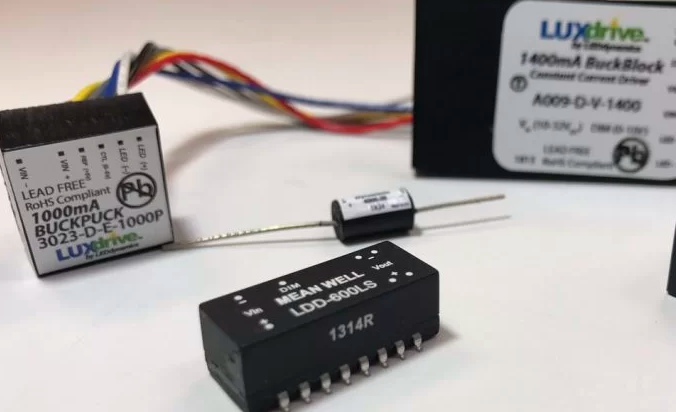
An LED driver is an electronic device that provides the necessary power and regulates the electrical current supplied to an LED or an array of LEDs. Unlike traditional incandescent or fluorescent bulbs that operate on standard voltage and can directly connect to a power source, LEDs require a constant current of electricity to maintain optimal performance. The LED driver ensures that this constant current is delivered, preventing fluctuations in voltage or power that could otherwise damage the LEDs or shorten their lifespan.
LED drivers are available in various designs and types, each suited for specific applications and requirements. They are commonly found in indoor and outdoor lighting fixtures, automotive lighting, and other devices that incorporate LEDs.
Why Are LED Drivers Important?
LEDs are designed to operate on low-voltage direct current (DC) power, but they are often powered by alternating current (AC) from a regular power outlet. This is where the led driver comes into play. It acts as a converter that changes the incoming AC voltage to the required DC voltage and current that the LED needs to function efficiently. The LED driver also regulates the power flow to ensure that the LED receives the appropriate current without being overdriven or underdriven, both of which can cause issues such as flickering or premature failure.
In addition to power regulation, LED drivers also offer several other benefits:
- Dimming Control: Many LED drivers are designed with dimming functionality. This means that they can adjust the brightness of the connected LEDs according to user preferences, offering flexibility in lighting designs and enhancing energy efficiency by lowering power consumption when full brightness is not needed.
- Safety: LED drivers often include safety features such as overload protection, short-circuit protection, and thermal protection to prevent damage to both the driver and the LEDs in case of faults or malfunctions.
- Improved Longevity: By providing the correct amount of power and regulating electrical current, LED drivers help extend the lifespan of LEDs. Poor regulation can lead to premature burnout of the LED, but a high-quality driver ensures that the LED operates within its optimal parameters, thereby maximizing its operational life.
Types of LED Drivers
LED drivers come in two primary types: constant current drivers and constant voltage drivers. Understanding the differences between these two is essential for choosing the right driver for a specific LED application.
1. Constant Current LED Drivers
Constant current LED drivers are the most commonly used type of LED driver. These drivers supply a fixed amount of current, which is necessary to power LEDs that are designed to operate at a specific current rating. LEDs are typically designed to work with a particular amount of current to achieve the desired brightness, and any variation can affect their performance or lifespan. The constant current driver ensures that the current remains stable and does not exceed or drop below the LED’s required level.
These drivers are often used in applications where the number of LEDs and their configuration are fixed, such as street lights, high-bay lighting, and recessed ceiling lights. They are ideal for lighting systems that require precise control over the current, ensuring that each LED performs optimally.
Read also: Balancing Technology and Human Touch: A Guide to Successful Self-Ordering System Implementation
2. Constant Voltage LED Drivers
In contrast to constant current drivers, constant voltage LED drivers supply a fixed voltage to the LED. These drivers are typically used for LED strips, signage, and other applications where the LEDs are arranged in parallel, and each LED operates independently. Since the voltage remains constant, these drivers are suitable for setups where the LED strips or arrays are designed to operate at a specific voltage, often 12V or 24V.
Constant voltage drivers are generally easier to work with for DIY projects and installations because the voltage remains stable regardless of the current drawn by the LED array. However, they may not be suitable for all LED applications, as they can be less efficient in managing power delivery compared to constant current drivers.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an LED Driver
Selecting the right LED driver for a particular application is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. There are several factors to consider when choosing an LED driver:
- Power Requirements: Ensure that the driver provides the appropriate power output (in terms of voltage and current) for the specific LEDs being used. Each LED has a recommended operating range for voltage and current, and using a driver that does not match these requirements can lead to malfunction or reduced lifespan.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of an LED driver determines how much of the electrical energy supplied to it is converted into usable power for the LEDs. High-efficiency drivers will minimize energy wastage, reduce heat generation, and lower electricity bills.
- Compatibility: Not all LED drivers are compatible with every type of LED. It is essential to verify that the driver is designed for the specific LED type, whether it is constant current or constant voltage, and whether it works with the intended LED configuration.
- Dimming Capabilities: If dimming is required, ensure that the LED driver supports dimming features and is compatible with the dimming control systems (e.g., triac dimmers, 0-10V dimming). Not all drivers are dimmable, and using an incompatible driver may result in flickering or other issues.
- Size and Form Factor: LED drivers come in different sizes and configurations. Choose a driver that fits the available space and is suitable for the installation environment. For example, outdoor installations may require a driver that is weather-resistant or has a higher IP rating.
- Safety Certifications: Always choose an LED driver that is certified by recognized safety standards, such as UL, CE, or ETL. This ensures that the driver has been tested for safety, quality, and compliance with international electrical standards.
The Future of LED Drivers
As LED technology continues to evolve, so too does the design and functionality of LED drivers. Future LED drivers are likely to integrate smarter features, such as wireless control, IoT connectivity, and improved energy management systems. These advancements will allow for more sophisticated lighting control, enabling users to manage lighting systems more efficiently and effectively.
Moreover, the integration of LED drivers with smart city infrastructure and automation systems will likely play a significant role in the development of future urban lighting networks. The ability to monitor and control street lighting remotely and optimize energy consumption in real-time will help create more sustainable and cost-effective lighting solutions for cities worldwide.
Conclusion
LED drivers are an indispensable component of LED lighting systems, ensuring that the LEDs receive the correct power and operate efficiently over their lifespan. Choosing the right LED driver is essential for maintaining optimal lighting performance and achieving energy savings. Whether you’re installing a residential lighting system or a large-scale commercial or industrial lighting solution, understanding the different types of drivers and their specifications will help you make the best decision for your lighting needs. As technology continues to advance, LED drivers will become increasingly sophisticated, offering smarter and more energy-efficient solutions for all lighting applications.